Restaurant employees and managers understand the importance of preventing foodborne illness. It’s important to keep this knowledge fresh, so we’ve prepared some fun, educational questions to help keep cleanliness top of mind. How does your knowledge of this ever-expanding topic stack up? Take our quiz to find out!
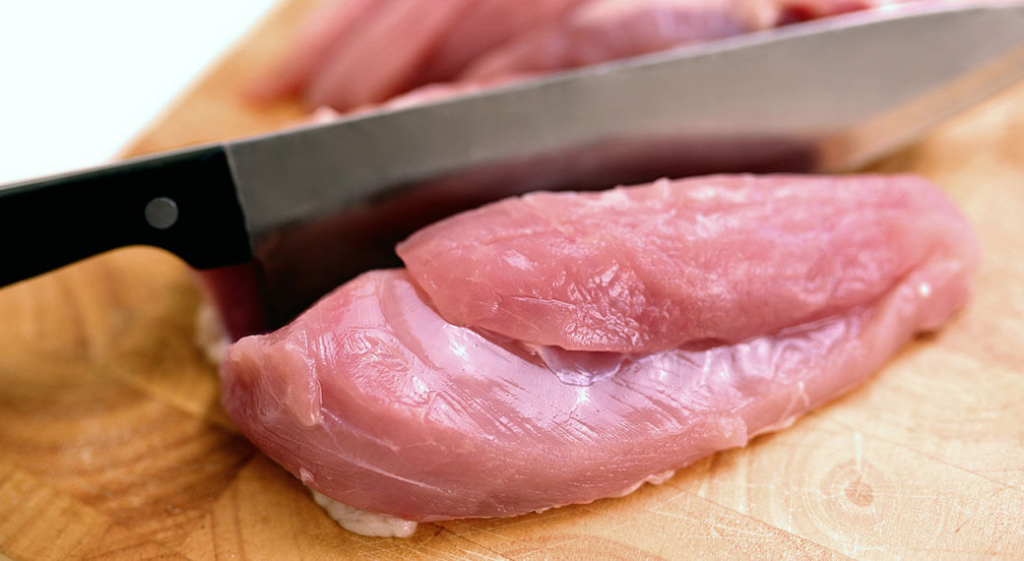
According to the FDA, what are the four key steps to food safety?

Follow the 4 key steps to food safety: Always — Clean, Separate, Cook, and Chill. (https://www.fda.gov/food/food-safety-during-emergencies/best-practices-retail-food-stores-restaurants-and-food-pick-updelivery-services-during-covid-19#employeehygiene)
According to the US Department of Agriculture's Food Safety and Inspection Service (FSIS), which group isn’t susceptible to foodborne illness and serious side effects?

People with cancer, diabetes, kidney disease, HIV/AIDS, or an organ transplant—as well as healthy older adults and pregnant women—who have weakened immune systems are at increased risk for foodborne illness. (https://www.usda.gov/media/blog/2012/08/08/fsis-and-fda-offer-risk-food-safety-brochures)
Which type of cow’s milk is considered lower risk for foodborne disease?
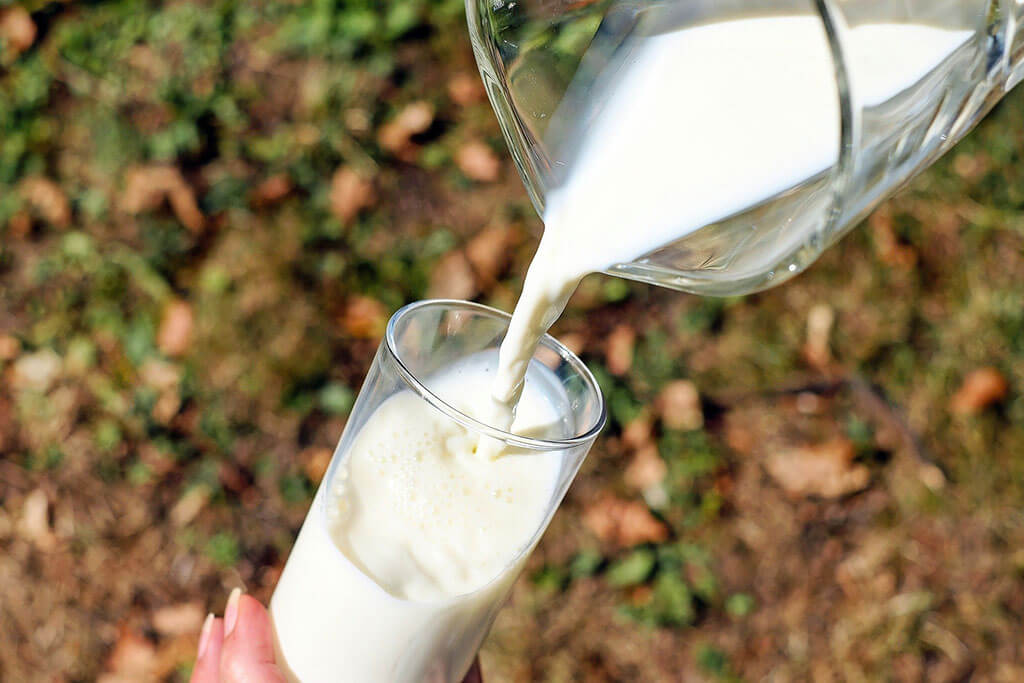

Pasteurization effectively kills raw milk pathogens without any significant impact on milk nutritional quality.(https://www.fda.gov/food/buy-store-serve-safe-food/raw-milk-misconceptions-and-danger-raw-milk-consumption)
Bacteria, mold, fungus, and viruses are examples of:
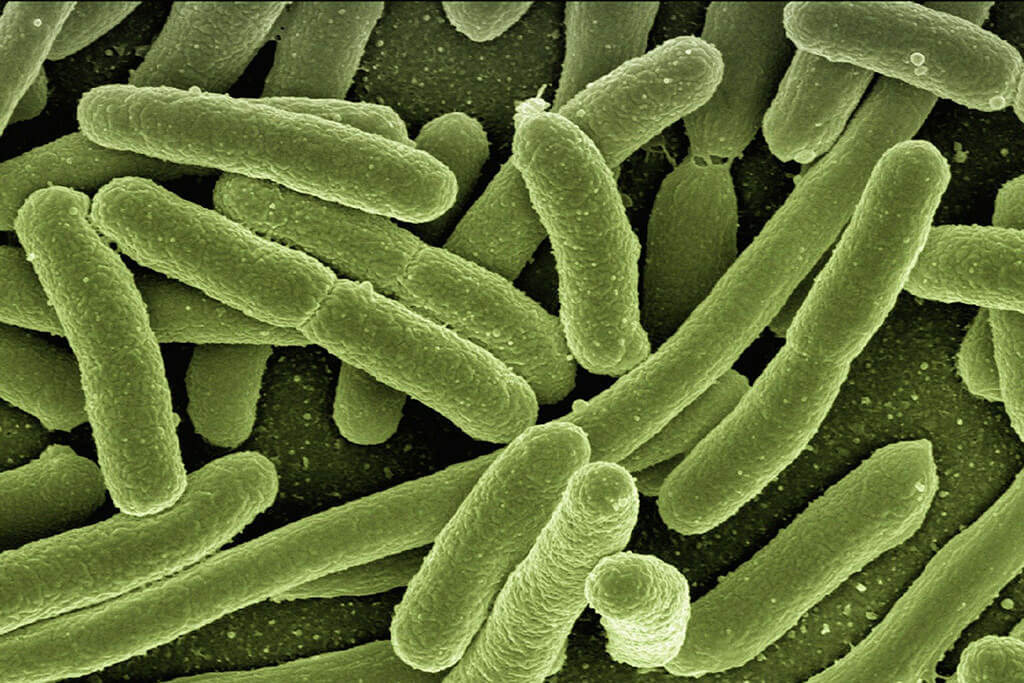
The main types of pathogens transmitted in food. (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Food_safety)
According to the CDC, which practice contributes to nearly half of all restaurant related breakouts?

Food handling by a sick worker contributes to nearly half of all restaurant-related outbreaks.(https://www.cdc.gov/nceh/ehs/ehsnet/plain_language/index.htm)
The CDC lists which practice as dangerous when cooling foods?

Hot food needs to be cooled quickly to prevent foodborne illness outbreaks caused by germs. Ten years of data (1998 to 2008) show 504 outbreaks of foodborne illness in restaurants were caused by hot food cooled too slowly.(https://www.cdc.gov/nceh/ehs/ehsnet/plain_language/food-cooling-improvements.html)
Restaurants with managers certified in food safety are more likely to experience:

Positive media coverage. (https://www.cdc.gov/nceh/ehs/publications/kmc-infographic.html)
What is the Food Code?

The U. S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) publishes the Food Code, a model that assists food control jurisdictions at all levels of government by providing them with a scientifically sound technical and legal basis for regulating the retail and food service segment of the industry (restaurants and grocery stores and institutions such as nursing homes). Local, state, tribal, and federal regulators use the FDA Food Code as a model to develop or update their own food safety rules and to be consistent with national food regulatory policy. (https://www.fda.gov/food/retail-food-protection/fda-food-code)
How many foodborne diseases have researchers discovered?

Researchers have identified more than 250 foodborne diseases.(https://www.cdc.gov/foodsafety/foodborne-germs.html)
According to the CDC, Campylobacter is:

People can get Campylobacter infection by eating raw or undercooked poultry or eating something that touched it. They can also get it from eating other foods, including seafood, meat, and produce, by contact with animals, and by drinking untreated water. Campylobacter infection is the most commonly identified cause of Guillan-Barré syndrome.(https://www.cdc.gov/campylobacter/)



